Faced with evolving societal expectations and growing regulatory pressure, the energy transition has become a major strategic priority for industrial companies. Reducing carbon footprints, optimizing energy consumption, and integrating more renewable sources are no longer optional, they are now structural priorities.
In this context, mastering the sustainability of maintenance equipment becomes a key driver for achieving this transformation. Every action carried out in the field must be measurable, documented, and geared toward sustainable performance.
This is precisely where CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems) plays a central role. Far more than just a tool for tracking operations, it becomes a true strategic lever for driving the energy transition by incorporating performance indicators. This enables in-depth analysis of field data and ensures intelligent, eco-responsible maintenance.
Energy Transition: More Than Just an Environmental Goal
The energy transition refers to all transformations aimed at reducing dependence on fossil fuels, developing renewable energy sources, and improving energy efficiency. It is part of a global movement to combat climate change, but its scope extends far beyond the environmental dimension alone.
Industrial companies, infrastructure operators, and local authorities are now facing new regulatory requirements, environmental standards, ESG reporting, and decarbonization laws, that demand a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. This creates the need for better resource management and increases pressure from stakeholders (customers, partners, and citizens) to adopt a more responsible model.
However, this transformation comes with many challenges:
- – Aging industrial assets make it difficult to control energy performance.
- – Excessive energy consumption increases both operational costs and environmental impact.
- – Lack of visibility on equipment performance hinders optimization efforts.
The maintenance of equipment, buildings, and infrastructure has a direct impact on the environment. Without proper management, it can lead to:
- – Excessive energy consumption from poorly maintained equipment
- – Increased technical interventions and travel, with a significant carbon footprint
- – Inefficient management of spare parts and inventories
- – Difficulty ensuring compliance with environmental regulations
In the face of these issues, the digitalization of maintenance, driven by tools like CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems), emerges as an essential lever for initiating a structured, sustainable, and measurable energy strategy.
The Strategic Role of CMMS in the Energy Transition
A CMMS enables organizations to centralize, plan, track, and analyze all activities related to equipment maintenance. It is a strategic tool to support organizations in their energy transition.
In Practical Terms: Key CMMS Features That Directly Support Energy Performance and Sustainability Goals
- Monitoring energy consumption : Consumption data can be linked to each piece of equipment, allowing you to identify anomalies, analyze the most energy-intensive assets, and implement targeted corrective actions.
- Scheduling preventive maintenance : Well-planned maintenance prevents malfunctions that cause excessive energy use, while also optimizing intervention schedules.
- Extending asset lifespan : By ensuring regular and intelligent upkeep, CMMS minimizes premature wear and avoids costly, resource-intensive replacements.
- Reducing energy-intensive breakdowns : Unplanned downtime often leads to energy spikes or heavy start-up loads. CMMS helps anticipate and reduce these incidents.
- Complete traceability of actions : Every operation is recorded and logged, making it easier to meet environmental audit requirements and demonstrate the organization’s commitment to sustainable management.
- Lowering the carbon footprint through predictive maintenance : By analyzing historical data, failures can be detected before they cause interruptions or energy-heavy repairs. Accurate diagnostics make it possible to replace only the necessary parts, reducing waste and limiting the overuse of raw materials.
- Better inventory management :Spare parts needs are better anticipated, reducing excess stock and warehouse waste.
- Reducing travel and digitizing documentation : By digitalizing technical processes and centralizing information, CMMS reduces unnecessary field travel. Technicians can access real-time data via mobile apps, consult intervention histories remotely, and optimize their routes to avoid unnecessary trips.
Through these features, CMMS becomes a true ally in implementing an energy strategy that is efficient, measurable, and aligned with today’s sustainability expectations.
Sustainable Practices in Industrial Operations
Next-generation CMMS solutions integrate dedicated modules to track environmental indicators and generate CSR/ESG reports. They act as catalysts for implementing concrete environmental policies:
- – Promoting the circular economy and resource recovery : CMMS supports the adoption of circular economy practices by ensuring precise tracking of inventory and spare parts. It enables the reuse of parts in good condition, prioritizes recycled or refurbished components, and optimizes technical waste management. This precise oversight reduces waste and maximizes resource utilization, fully aligning with a sustainable, circular approach.
- – Tracking environmental certifications : Complete intervention traceability makes it easier to comply with ISO 14001, ESG, and other environmental standards.
- – Smart energy management : Some CMMS systems can connect to consumption sensors to monitor real-time use of water, gas, or electricity.
These data are invaluable for compiling environmental reports and meeting ISO or regulatory requirements, such as France’s “Décret Tertiaire.” They also support informed decision-making and adjustments to environmental action plans.
Adopting a CMMS benefits not only the environment but also the people who operate and maintain the assets. By ensuring rigorous equipment upkeep, CMMS helps reduce workplace accidents, making facilities safer for employees and lowering indirect costs related to incidents.
Moreover, daily CMMS use raises awareness among teams about industrial ecology issues, gradually fostering a more sustainable and responsible corporate culture.
The Impact of the Energy Transition on Businesses
Companies are under increasing pressure from multiple stakeholders to adopt more sustainable practices. Investors, for instance, are projecting $53 trillion in sustainable investments by the end of 2026, pushing organizations to reassess their priorities. From the consumer side, 80% say they prefer products from responsible companies, directly influencing production and communication strategies. Employees, particularly younger talent, are also a driving force, with 64% stating they choose their employer based on environmental commitments. Finally, governments are tightening regulatory pressure, with 38 of the world’s 50 largest economies now requiring environmental reporting.
In this shift toward a more sustainable model, companies are actively seeking concrete solutions to meet the expectations of investors, consumers, employees, and regulators. This is precisely where CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems) can play a strategic role. Beyond its traditional functions, it becomes a true tool for driving environmental performance.
A study conducted by the University of California (UC) found that an industrial company was able to reduce its energy consumption by 8% by detecting and correcting overheating anomalies using CMMS.
Similarly, Carnegie Mellon University studied air conditioning optimization through such a system, observing a 4% reduction in overall energy consumption.
Another report states that preventive maintenance scheduled via CMMS can reduce energy consumption by 5% to 15% in modernized industrial processes, particularly through the integration of predictive technologies such as IoT, connected sensors, and predictive maintenance.
These figures confirm that CMMS is not limited to maintenance, it also serves as a powerful lever for energy optimization.
IBM Maximo and CARL Software: Two Allies for Eco-Efficient Maintenance
- Identifying Consumption Peaks and Acting Quickly with CARL Source
CARL Source includes real-time energy monitoring modules that enable technical managers to:
- – Visualize periods of high consumption
- – Correlate peaks with specific events or malfunctions
- – Adjust settings or usage to reduce costs
This responsiveness allows corrective actions to be implemented quickly, before excessive consumption becomes a structural issue.
- IBM Maximo: A Powerful Lever for Reducing Energy Costs
Sustainability is no longer just an environmental concern—it is now a strategic imperative and a genuine economic opportunity for businesses. Those who succeed in leveraging it as a performance driver will be the winners of tomorrow.
In this context, the IBM Maximo Application Suite (MAS) plays a key role. Why? Because industrial assets,precisely the type MAS is designed to manage, account for 76% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, or around 1.6 billion tons per year, according to official data from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
IBM Maximo Application Suite helps companies achieve substantial energy savings by improving equipment performance and reducing unplanned downtime. With intelligent planning based on real-time data, energy savings can reach up to 20%.
IBM Maximo transforms asset management into a strategic driver of both environmental and economic performance.
Organizations gain access to a complete suite for managing assets in a smart, sustainable, and compliant way. It serves as a true catalyst for reducing costs, improving operational performance, and meeting ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) requirements.
IBM Maximo simplifies the collection, analysis, and reporting of ESG indicators, including:
- – Tracking carbon emissions
- – Environmental compliance reporting
- – Monitoring energy and water consumption
- – Integration with carbon footprint calculation APIs
- – Improved visibility into suppliers and subcontractors across the MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operations) supply chain
Reducing Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions with IBM Maximo
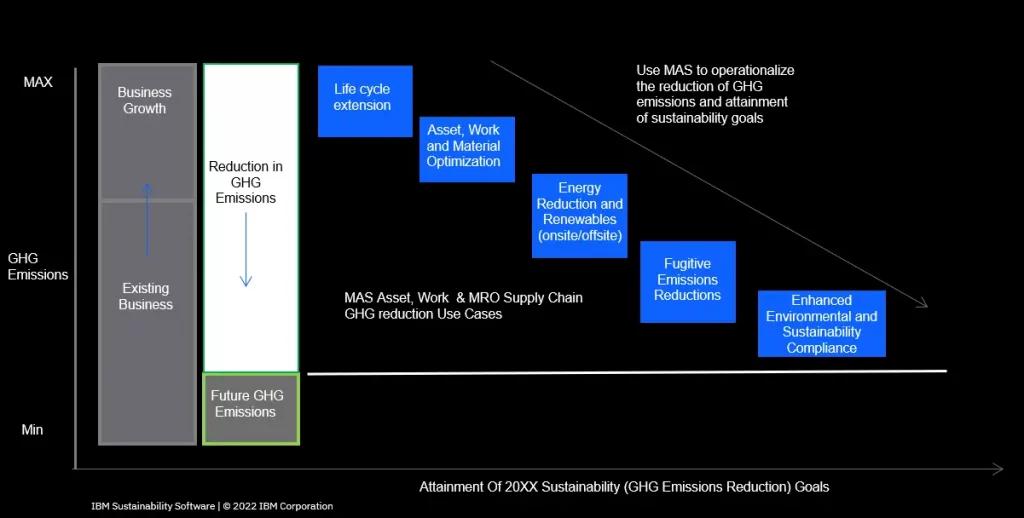
This diagram illustrates how IBM Maximo Application Suite (MAS) helps progressively reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions while supporting business growth. By enabling the measurement, monitoring, adaptation, and automation of emission reductions across the entire asset portfolio, MAS becomes a strategic tool for managing sustainability. It allows organizations to:
- – Extend asset lifespan by 10 to 15%
- – Reduce maintenance costs by 15 to 20%
- – Increase wrench time (effective work time) by 10 to 30%
- – Reduce emissions and waste at the operational level
- – Capture high-quality data at the asset level and automate audits, compliance, and sustainability reporting
Conclusion: CMMS as a Key Enabler of the Energy Transition
Adopting a CMMS means choosing a more responsible, higher-performing industry that is better prepared for tomorrow’s challenges. By improving resource management, preventing failures, reducing waste, and ensuring compliance with environmental standards, CMMS establishes itself as an essential pillar of the energy transition.
Far more than a simple planning tool, CMMS becomes a strategic ally for technical and CSR departments in implementing an eco-responsible maintenance policy.
Ready to start your energy transformation? We’re here to support you at every step.
Références:
IBM – MAS Sustainability drop
Maximo sustainability in asset management
CARL Energy – Energy performance platform connected to your CMMS CARL Source



